At Tess AI, your agents can go way beyond static knowledge. With the Advanced Web Data Extraction Steps, you can turn them into smart researchers, able to fetch up-to-date information directly from the internet.
This guide will show you how to set up your agents to find job openings, compare product prices, search for news and much more, in a fully automated way.
What are the Web Data Extraction Steps?
The Advanced Steps are building blocks that you add to your agent’s logic in the AI Studio. The Web Data Extraction category groups a series of steps designed to run searches on different online platforms
Instead of a generic search, these steps let you create highly customized and targeted queries, improving the agent’s training with up-to-date and relevant information. The options include:
Google Organic Search: For general searches, news and information.
Google Shopping Search: To search for products and compare prices.
Google Jobs Search: To find job openings.
Amazon Product Search: To search for products directly on Amazon.
And many others.
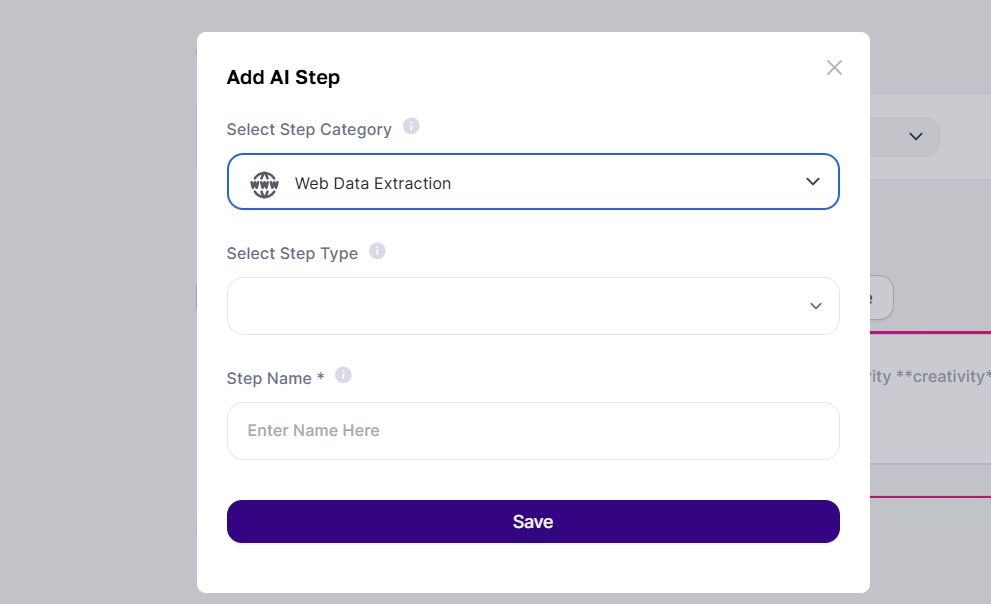
How to Set Up an Agent with Web Search
Access Agent Studio and start creating or editing an agent.
Add an Advanced Step: On the creation screen, find the "AI Steps" section and add a new step.
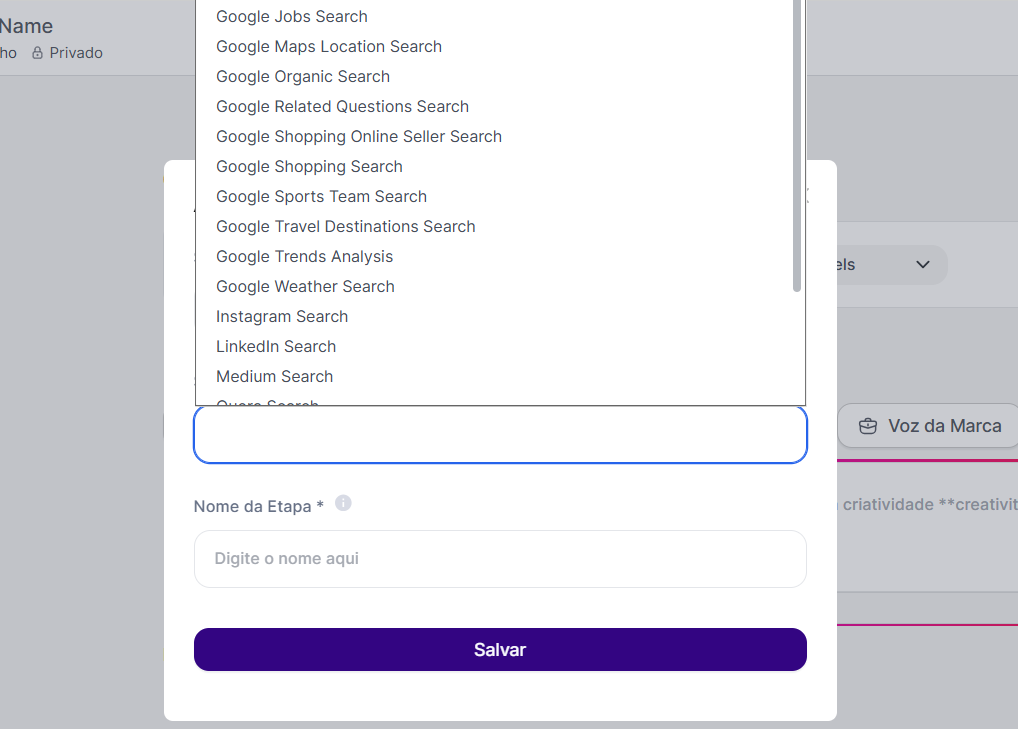
Select the Step Type: Choose the Web Data Extraction category and then the desired search type (e.g.: Google Shopping Search).
Set Up the Search: Fill in the specific search fields. For example, the name of the product you want to search for. At this step, you can either leave some of the requirements preconfigured as default, or use the user definition to create inputs and keep this field variable.
For example, if the domain always needs to be Brazil, you can already configure it. Or if the product has to have a specific name, you can already fill it in. Otherwise, either enable user decision, or create inputs and reference them in the specific fields.
Set the Step Name: This is a crucial step. Give a name to the result of your search (e.g.: product search). This name will become the variable you’ll use in your prompt to access the collected data.
With that, the research stage is done. Now, the secret is to connect this stage to a good prompt.
Practical Example: Promotion Search Agent
Let’s create an agent that finds the best deals on Google Shopping.
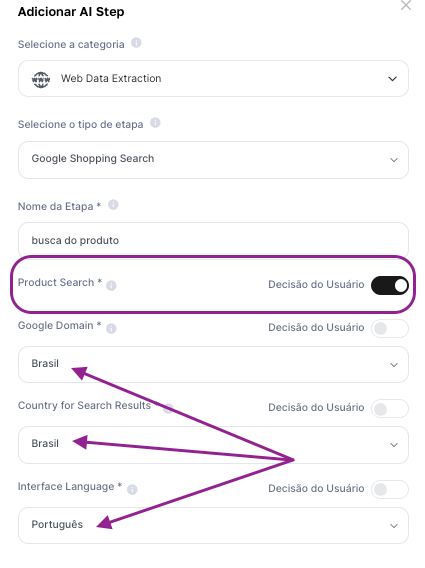
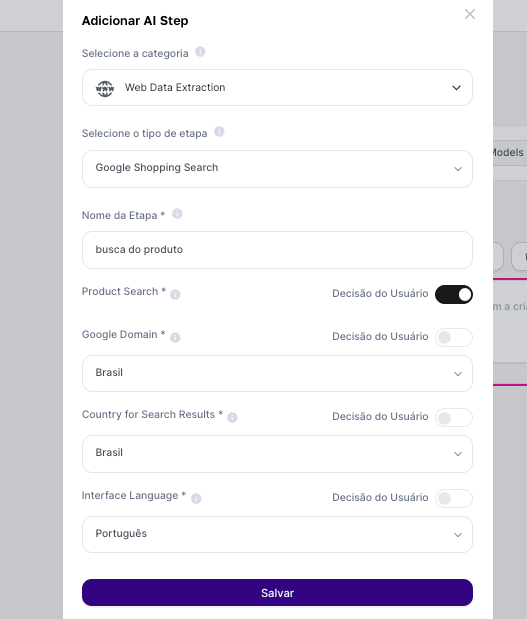
1. Step configuration:
Step Type: Google Shopping Search
Product Search: A variable can be used here
Domain and Language: Brazil and Portuguese
Step name: product search
2. The Command Prompt (The Brain of the Operation)
The Advanced Step gets the raw information. Your prompt is what turns that information into a useful and smart answer.
Suggested Prompt:
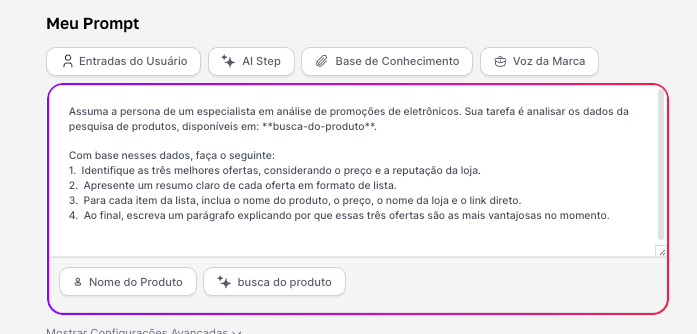
Assume the persona of a specialist in analyzing electronics promotions. Your task is to analyze the product research data, available at: **busca-do-produto**.
Based on this data, do the following:
1. Identify the three best deals, considering the price and the store's reputation.
2. Present a clear summary of each deal in a list format.
3. For each item in the list, include the product name, price, store name, and direct link.
4. At the end, write a paragraph explaining why these three deals are the most advantageous at the moment.
When you run the agent, it will first perform the search on Google Shopping (the Step) and then use the collected data to execute the instructions from your prompt.
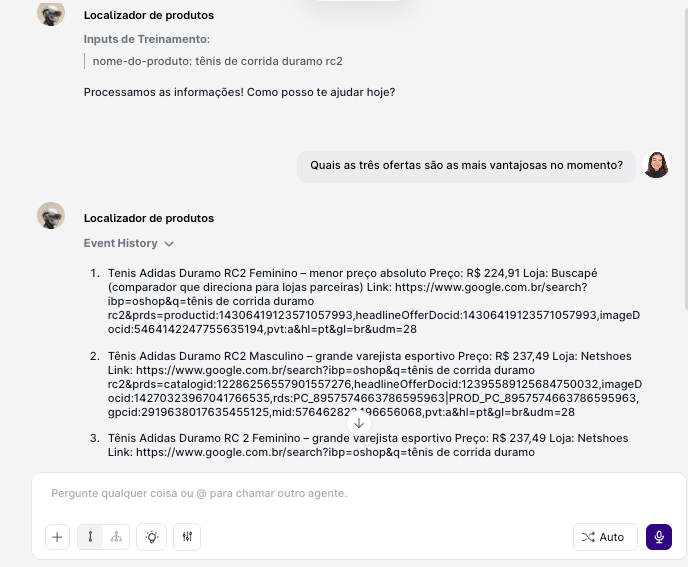
Tips:
The Prompt Is the Brain: Be detailed in your instructions. The Step collects the data; the prompt analyzes it. The clearer the prompt, the better the analysis.
Be Specific in Your Search: The more specific your query in Step (e.g., "iPhone 15 128GB Black" instead of "iPhone"), the more relevant the results will be.
Integrating web data extraction Steps turns your static repository agents into dynamic assistants. By mastering the combination of research steps with detailed prompts, you can create powerful tools to automate market research, monitor news, and save valuable time.